CBD and the Modern Age of Anxiety
In an era defined by technological advancement and incessant streams of information, the world has never been as interconnected. Yet, paradoxically, as we’ve grown more connected digitally, many have felt a growing sense of isolation, stress, and unease. Anxiety, a complex and multifaceted emotional and physiological response to stress, has emerged as one of the predominant mental health challenges of the 21st century. It’s an issue that transcends geographical borders, socio-economic classes, and age groups. With the rise in anxiety disorders, there has been a concerted search for treatments and remedies, both traditional and alternative. One such alternative that has surged in popularity in recent years is CBD, or cannabidiol. This blog post will be a deep dive into the use of CBD for anxiety.
Anxiety, in its essence, isn’t just an occasional wave of unease or nervousness before a significant event; it’s a more persistent, overwhelming, and sometimes debilitating emotion. In its clinical manifestations, anxiety disorders can present as generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and several other forms. These disorders don’t merely impact the mind but can also have physical symptoms such as increased heart rate, tremors, and digestive issues.
The numbers speak for themselves. According to the World Health Organization, an estimated 264 million people worldwide suffer from an anxiety disorder. This is not a minor blip or a passing trend; it’s a glaring testimony to the scale and depth of the issue. Factors contributing to this rise can be myriad, from personal traumas and genetic predispositions to environmental stressors like financial pressures, work-related stress, and the relentless pace of modern life.
In tandem with the rise in anxiety, there’s also been an increasing skepticism regarding traditional pharmaceutical treatments. Concerns range from side effects of medications to the potential for dependency and the often prohibitive costs associated with long-term drug therapies. This has set the stage for alternative remedies to shine, and few have captured public attention and interest as robustly as CBD.
CBD, or cannabidiol, is a natural compound found in the cannabis plant. Unlike its more notorious cousin, THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), CBD doesn’t produce the “high” or euphoria associated with marijuana. Instead, it offers a plethora of health benefits without the psychoactive effects, making it an attractive option for those looking for relief without intoxication.
Over the past decade, the narrative around cannabis and its derivatives has shifted dramatically. No longer relegated to hushed conversations and the fringes of alternative medicine, CBD has found its way into mainstream dialogue, primarily due to its potential therapeutic properties. From wellness influencers and health gurus to respected researchers and clinicians, many are now touting the benefits of CBD for a range of ailments, with anxiety being at the forefront.
CBD’s rise in the wellness world isn’t just anecdotal. Preliminary scientific studies have started to substantiate some of the claims made by early adopters. These studies suggest that CBD might play a role in modulating the body’s response to stress, potentially by interacting with serotonin receptors, which are crucial in regulating mood and behavior.
However, the conversation around CBD isn’t just about its potential benefits. It’s equally about a cultural shift towards natural and holistic remedies. The modern individual, empowered with information at their fingertips, is more discerning and inquisitive about what they put into their bodies. They’re seeking treatments that align with their values, lifestyles, and an overarching philosophy of wellness. In this milieu, CBD represents more than just a compound; it symbolizes a broader move towards natural, sustainable, and conscious living.
Understanding Anxiety
Anxiety, a term frequently used in our daily lexicon, represents a spectrum of emotional and physiological states, ranging from a fleeting feeling of unease to chronic and debilitating disorders that can profoundly impact daily life. It’s essential to distinguish between routine stress or nervousness and clinically recognized anxiety disorders. The latter often impede normal functioning and require targeted interventions.
Definition and Symptoms
At its core, anxiety can be described as a feeling of apprehension or fear about what’s to come. Everyone has, at some point, experienced the flutter in the stomach before a significant event or the pounding heart in a stressful situation. However, anxiety disorders magnify these sensations, making them persistent, intense, and often appearing without a clear immediate cause.
The symptoms of anxiety can be both psychological and physical. The most common psychological symptoms include:
For a diagnosis of generalized anxiety disorder (one of the many forms of anxiety disorders), individuals would typically experience persistent worrying or anxiety for at least six months, and have several of the psychological and physical symptoms.
Common Causes and Triggers
Anxiety doesn’t originate from a singular source. It’s the culmination of various factors, a complex interplay of biological, environmental, psychological, and developmental elements.
Biological Factors: Genetics can play a role, meaning individuals might inherit a predisposition to anxiety disorders. Certain brain structures and neurotransmitter imbalances have also been associated with heightened anxiety.
Environmental Factors: External triggers and stressors can precipitate or exacerbate anxiety. These might include:
Traditional Treatments for Anxiety
Over the years, a broad array of treatments has been developed for anxiety, ranging from therapeutic interventions to pharmacological solutions:
Psychotherapy (Talk Therapy): This involves speaking with a therapist to address emotional and psychological roots of anxiety. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), in particular, has been found effective for treating anxiety disorders. CBT teaches individuals to recognize and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that lead to anxious feelings.
Medication: There’s a range of drugs prescribed for anxiety:
Lifestyle Changes: Sometimes, addressing lifestyle factors can help manage anxiety. This might involve reducing caffeine intake, getting regular exercise, practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation, and ensuring adequate sleep.
Alternative Therapies: Techniques such as meditation, acupuncture, and deep-breathing exercises can help focus the mind and reduce anxiety and other stressful feelings.
In sum, understanding anxiety necessitates recognizing its multifaceted nature, causes, and the myriad of available treatments. With an increase in global awareness and ongoing research, treatments have evolved, offering hope and respite to those affected. As with any condition, early intervention, an informed approach, and seeking professional guidance can significantly affect outcomes.
How CBD Works in the Body
The fascination surrounding CBD, especially its potential therapeutic benefits, has sparked rigorous investigations into how it functions within the human body. A closer look at the mechanisms through which CBD operates reveals a complex interplay with the endocannabinoid system, serotonin receptors, and distinct differences from traditional anti-anxiety medications.
The Endocannabinoid System and Its Role in Mood Regulation
Every human being possesses an intricate system known as the endocannabinoid system (ECS). Discovered in the 1990s, this system is named after the plant that led to its discovery, cannabis. The ECS plays a pivotal role in maintaining homeostasis, which means it helps keep a stable internal environment despite external changes. This involves regulating a wide array of functions, from sleep, appetite, and pain to, importantly for our discussion, mood.
The ECS is composed of three primary components:
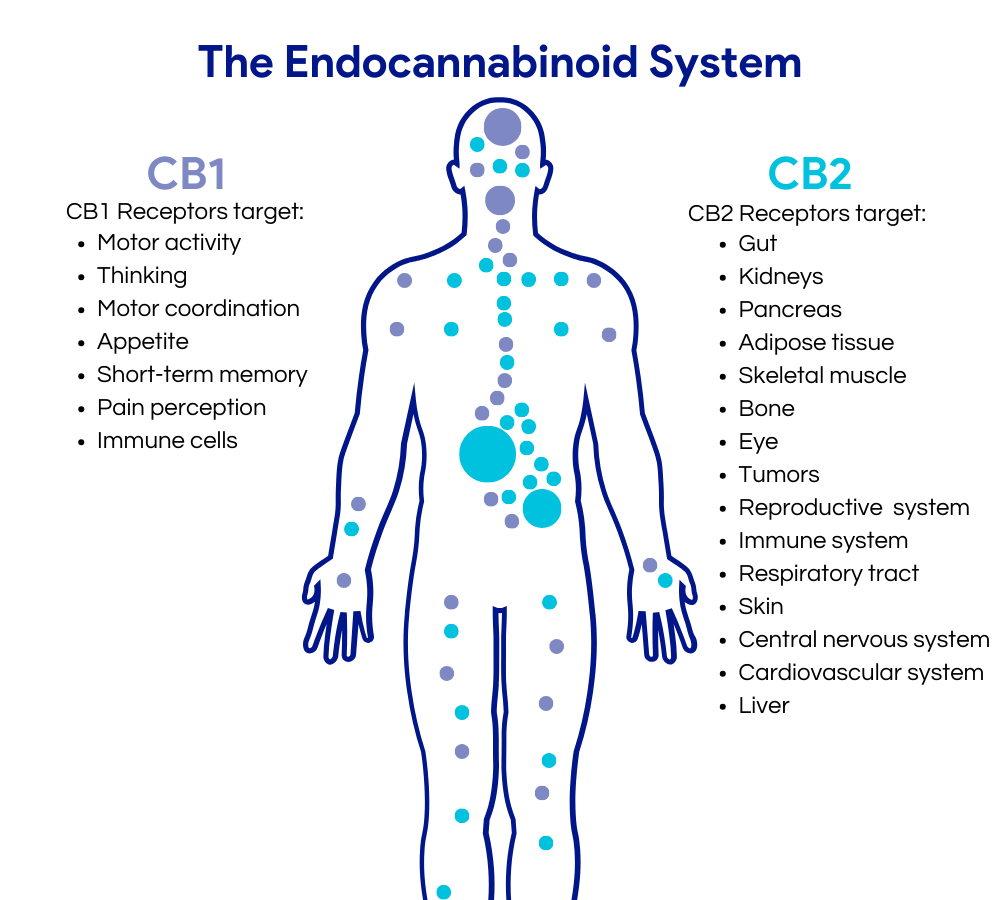
In the context of mood regulation, anandamide is often referred to as the “bliss molecule” and plays a crucial role in producing feelings of happiness and well-being. When the ECS is functioning optimally, there’s a balance of endocannabinoids effectively regulating mood. However, if there’s an imbalance – say, a shortage of anandamide – feelings of anxiety or depression might manifest.
CBD’s Interaction with Serotonin Receptors
Beyond the ECS, CBD also interacts with other systems in the body. One of the most noteworthy interactions is with the serotonin system. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter responsible for mood regulation, among other functions. Low levels of serotonin are often associated with mood disorders, particularly depression, but also anxiety.
CBD is believed to interact with the 5-HT1A receptor within the serotonin system – a subtype of the serotonin receptor. While the precise mechanisms are still under investigation, some studies suggest that CBD might enhance the signaling through serotonin receptors. By doing so, CBD could potentially boost serotonin levels in the brain, acting similarly to serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) like Prozac and Zoloft, which are commonly prescribed for anxiety and depression.
The Difference in How CBD Works Compared to Traditional Anti-Anxiety Medications
Traditional anti-anxiety medications, such as benzodiazepines and SSRIs, function differently than CBD.
Benzodiazepines enhance the effect of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) at the GABA-A receptor, resulting in sedative, hypnotic (sleep-inducing), anxiolytic (anti-anxiety), anticonvulsant, and muscle relaxant properties. However, they come with side effects like potential dependence and tolerance.
SSRIs work by inhibiting the reuptake of serotonin in the brain, which increases the availability of serotonin in the synaptic space. This helps brain cells transmit more serotonin signals, which can reduce symptoms of anxiety and elevate mood in certain cases.
In contrast, CBD does not directly boost GABA or inhibit serotonin reuptake. Instead, its indirect interaction with the ECS and serotonin receptors provides a more holistic approach to mood regulation. One significant advantage of CBD over traditional medications is its lower potential for side effects. CBD doesn’t produce the same level of sedation, dependence, or withdrawal effects that some traditional medications might.
Moreover, the multi-faceted interaction of CBD – not just with the ECS and serotonin receptors but potentially with other neural systems – offers a broad-spectrum approach to mood regulation. This might be beneficial in addressing the underlying causes of anxiety, rather than merely suppressing symptoms.
Research on CBD and Anxiety
As the popularity of CBD has surged, so too has scientific interest in its potential therapeutic benefits, especially its effects on anxiety. The body of research is expansive, with studies ranging from animal models to human clinical trials, supplemented by countless anecdotes from individuals who’ve tried CBD for their anxiety. Here’s a brief overview of the current landscape of research on CBD and anxiety.
Human Clinical Trials
Human studies, though still in relatively nascent stages, have provided promising insights:
A 2019 study published in the journal Brazilian Journal of Psychiatry assessed the effects of CBD on individuals with social anxiety disorder (SAD) during a public speaking test. The participants who received CBD experienced significantly reduced anxiety, cognitive impairment, and discomfort in their speech performance compared to the placebo group.
Another study in 2011, focusing again on SAD, found that participants who took CBD had significantly decreased subjective anxiety, with brain scans showing changes in blood flow patterns in regions of the brain linked to feelings of anxiety.
While these studies are promising, they often involve small sample sizes. More large-scale, randomized trials are necessary to solidify the findings.
Let’s take a deeper look at some of the studies done on humans regarding the efficacy of CBD for the most common forms of anxiety:

Animal Studies
Animal models, particularly rodents, have been instrumental in elucidating potential mechanisms through which CBD might exert anxiolytic effects:
A review in the British Journal of Pharmacology in 2012 concluded that CBD can reduce various anxiety behaviors in rodents, including generalized anxiety, panic, obsessive-compulsive symptoms, and post-traumatic stress disorder.
Another study showed that CBD could increase the prefrontal cortex activation and serotonin levels in rats, providing a possible neurobiological mechanism for its anxiety-reducing effects.
Animal studies offer valuable insights into the potential pathways of CBD action, but translating these results directly to humans requires caution due to the inherent physiological and anatomical differences.
Subjective Reports and Anecdotes
While not as rigorous or controlled as structured studies, individual reports can provide a broader understanding of real-world applications:
Anecdotes from countless users have propagated the notion of CBD’s calming effects. Many report reduced feelings of anxiety, a heightened sense of calm, and improved sleep patterns after consuming CBD.
In a 2018 survey published in Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research, nearly 62% of CBD users reported using CBD to treat a medical condition, with anxiety being one of the top three reasons mentioned.
However, it’s essential to approach anecdotal evidence with a discerning eye, recognizing that individual responses can vary and might be influenced by factors like dosage, frequency, and the concurrent use of other medications or supplements.
Difference Between Short-Term and Long-Term Effects
Current research predominantly focuses on the immediate or short-term effects of CBD. These studies generally suggest a potential for acute symptom relief without the risk of major side effects.
How to Use CBD for Anxiety
Navigating the ever-expanding world of CBD products can be a challenge, especially when seeking relief from specific conditions like anxiety. There are various methods to consume CBD, each with its unique set of considerations. Understanding the different consumption methods, dosage nuances, and potential risks is crucial for those hoping to harness CBD’s therapeutic potential effectively.
Different Methods of Consumption:
Oils and Tinctures:
Description: CBD oils and tinctures are among the most popular formats. They consist of CBD extracted from the hemp plant, usually suspended in a carrier oil like coconut or hemp seed oil. The most powerful tinctures are made from nano-emulsified CBD, which is CBD whose particles have been broken down into tiny, nano-sized pieces that are much more easily absorbed by the body.
How to Use: The oil or tincture is typically administered sublingually (under the tongue) using a dropper. Holding the liquid there for a minute or so allows the mucous membranes to absorb the CBD, facilitating a relatively fast onset of effects.
Pros: This method offers quick absorption and allows easy dosage adjustment. It’s also a discreet way to consume CBD.
Cons: Some people may find the natural taste of CBD oil unpleasant, though flavored options are available. It is also recommended that you mix tinctures with food or drinks to make it more palatable.
Edibles:
Description: CBD edibles include any food or drink product infused with CBD. Gummies, chocolates, and beverages are popular choices.
How to Use: Consumed orally, much like any other food item.
Pros: They offer a tasty and inconspicuous way to consume CBD. The effects, although delayed, tend to be longer-lasting than some other methods.
Cons: The digestive process can decrease the amount of CBD that enters the bloodstream. There’s also a longer wait time to feel effects, which can lead individuals to consume more than necessary.
Vaping:
Description: Vaping involves inhaling CBD vapor produced by a vape pen or vaporizer device.
How to Use: CBD e-liquid or vape juice is loaded into the vaporizer, which then heats the liquid, turning it into vapor for inhalation.
Pros: Vaping ensures fast delivery as the CBD is absorbed directly into the bloodstream via the lungs.
Cons: There are concerns about the safety of vaping, with some studies suggesting it might harm lung health. The effects might also wear off faster than other methods.
Topical Applications:
Description: These are creams, balms, and lotions infused with CBD designed for direct application to the skin.
How to Use: Applied directly to the skin, especially areas of discomfort.
Pros: Ideal for localized relief, like tension knots that can accompany anxiety.
Cons: May not be as effective for systemic or full-body relief. Absorption rate can vary based on skin type and product formulation.

Download a free CBD Recipe E-Book from Zephyr Health Products.
Dosage Considerations:
Determining the right dosage can be tricky due to the absence of standardized guidelines. Factors like body weight, metabolism, and the nature of the anxiety symptoms play a role. It’s generally recommended to start with a low dose and gradually increase until the desired effect is achieved. Consulting with a healthcare professional familiar with CBD is always a good approach, especially for those new to the compound.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions:
While CBD is generally well-tolerated, some people might experience side effects, including:
CBD can also interact with certain medications, particularly those that come with a “grapefruit warning.” Both grapefruit and CBD interfere with cytochromes P450, a group of enzymes crucial for drug metabolism.
Benefits of Using CBD Over Traditional Medications
The rise in popularity of CBD as a potential therapeutic remedy, particularly for anxiety, can be attributed to several perceived advantages over conventional medications. As the conversation around mental health becomes increasingly nuanced, many are seeking alternative or complementary solutions that align with their values and experiences. Here are some benefits associated with choosing CBD over traditional medications for anxiety:
Fewer Side Effects:
Traditional anxiolytic medications, like benzodiazepines and SSRIs, can come with a host of side effects. These can range from fatigue, sexual dysfunction, and weight gain to more severe reactions like increased suicidal thoughts in some individuals.
CBD, on the other hand, is generally well-tolerated. While there can be side effects, such as dry mouth, diarrhea, or changes in appetite, they tend to be mild and less disruptive than those associated with some conventional medications.
No Risk of Dependency or Addiction:
One of the major concerns with benzodiazepines, in particular, is the potential for dependence and addiction. Prolonged use can result in increased tolerance, leading to higher dosages and, in some cases, a physical and psychological dependency.
CBD does not have the intoxicating effects associated with THC, another major compound found in cannabis. Furthermore, research thus far indicates that CBD has a low potential for abuse and dependence. This makes it an appealing option for those wary of developing a dependency on their anxiety medication.
Can Be Used in Conjunction with Other Treatments:
CBD can serve as a complementary approach. Some individuals find relief in combining the calming effects of CBD with other therapeutic interventions, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, meditation, or even other prescribed medications.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before combining treatments to ensure there are no harmful interactions or counterproductive outcomes.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of CBD are notable, it’s equally important to be aware of the challenges and considerations associated with its use:
The Need for More Comprehensive Research:
Despite the promising preliminary studies on CBD and its effects on anxiety, the research field is still relatively young. Many studies are based on small sample sizes or are short-term in nature.
For CBD to gain more widespread acceptance in the medical community, more comprehensive, large-scale, and long-term studies are needed. Until then, it’s crucial to approach claims about CBD’s efficacy with a balanced perspective.
Varied Quality and Concentration in CBD Products:
The booming CBD market has led to a plethora of products, but not all are created equal. The purity, quality, and concentration can vary widely from one product to the next.
Without standardized regulations in place, there’s potential for products that contain contaminants or do not have the advertised amount of CBD. Always opt for products that provide third-party lab results or are from reputable sources.
Legal Considerations Based on Where You Live:
While CBD derived from hemp (with 0.3% THC or less) is federally legal in the U.S., state laws can vary widely. In some places, CBD remains in a legal gray area or may even be illegal.
It’s vital to familiarize yourself with the laws in your region before purchasing or using CBD. Consideration should also be given when traveling, as the legality of possession can differ from one location to another.
Testimonials and Personal Experiences
The personal stories of those who have turned to CBD as a potential remedy for anxiety form a compelling narrative that speaks to its burgeoning appeal. These testimonials, however, are always best balanced with insights from experts in the mental health field.
Quotes and Stories from Individuals:
Rebecca, 28: “I started using CBD oil about six months ago. Before that, I was on a daily dose of an SSRI, but I still struggled with anxiety spikes. With CBD, I feel like there’s a calmness that wasn’t there before. It doesn’t make me feel ‘drugged’ or sleepy, just at ease.”
Martin, 34: “My therapist suggested I try CBD gummies as a complement to our sessions. I was skeptical at first, but the results have been undeniable. On tough days, the gummies provide a gentle buffer from my anxiety triggers.”
Anya, 23: “Vaping CBD became a game-changer for me during social events. I used to get extremely anxious in crowded spaces, but taking a few puffs helps me feel more grounded.”
Expert Opinions from Mental Health Professionals:
Dr. Elise Daniels, Clinical Psychologist: “While CBD isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution, many of my patients have found it beneficial as part of a broader therapeutic strategy. It’s crucial, though, to ensure that any CBD use is discussed within a clinical context.”
Dr. Rajan Mehta, Psychiatrist: “The endocannabinoid system’s role in mood regulation offers an exciting frontier for research. We’re only beginning to understand CBD’s potential, but the anecdotal evidence is certainly intriguing. As always, rigorous scientific investigation is key.”
Conclusion
CBD’s meteoric rise as a potential natural remedy for anxiety underscores a broader societal shift towards holistic health solutions. Its promise lies in its ability to potentially alleviate anxiety symptoms with minimal side effects and without the risk of addiction commonly associated with traditional pharmaceuticals.
However, as we’ve emphasized throughout this article, while the testimonials and preliminary research are promising, CBD is not a magic bullet. Its efficacy will vary from person to person, and it’s just one tool in the broader spectrum of anxiety management strategies.
If you’re considering trying CBD for anxiety, it’s paramount to consult with a healthcare professional first. They can provide guidance tailored to your specific situation, ensuring that you’re approaching its use in a safe and informed manner.
Further Reading & Resources
For those keen to delve deeper into the world of CBD and its potential therapeutic applications, here are some valuable resources:
Studies & Articles:
Brazilian Journal of Psychiatry: Cannabidiol in Anxiety and Sleep
British Journal of Pharmacology: Cannabidiol as a Potential Treatment for Anxiety Disorders
Reliable Sources for Purchasing CBD:
Zephyr Health Products – zhpcbd.com

Our mission is to provide the best quality products at a fair price. Our goal is to make products that help people and pets do more and feel better.
Give us a call at 732.446.3439
CBD For People and Pets